本文记录EventBus源码解析内容,版本为3.1.1,从几个核心方法依次入手,
register、post、postSticky、unregister。
EventBus
EventBus是Android和Java上的一个事件发布、订阅框架。
核心功能:
- 简化了组件之间的通信。
- 将事件的发送者跟接受者隔离。
- 同时适用于Activity、Fragment及后台线程。
- 避免了错综复杂的生命周期依赖。
- 使组价你通信代码变得更为简单。
- 通信速度快
- jar包小(~50k)
- 超过100000000+的应用使用。
- 可以定义接受者的优先级等其他辅助功能。
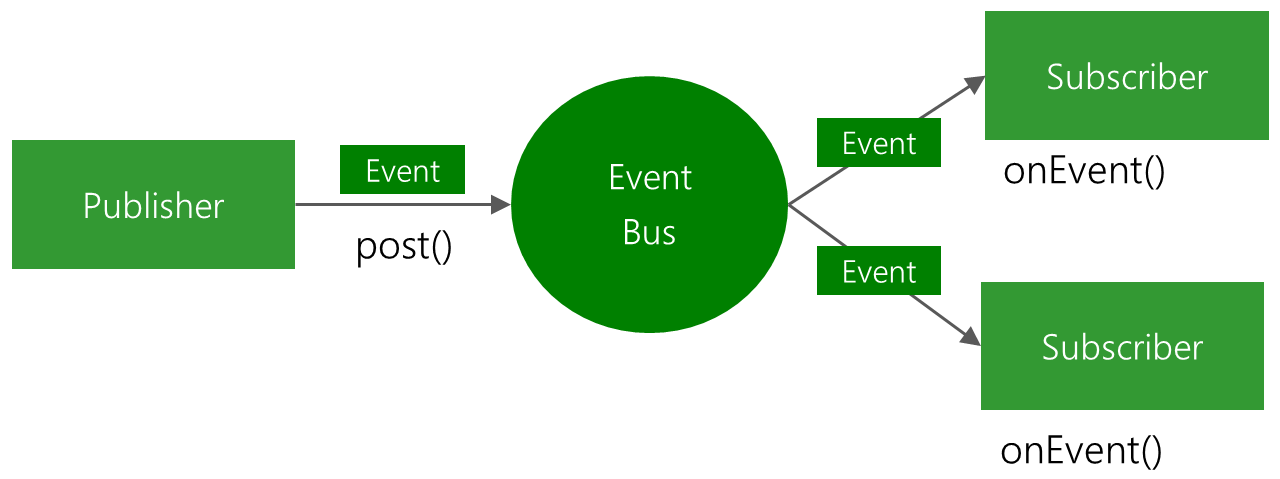
流程图如下:
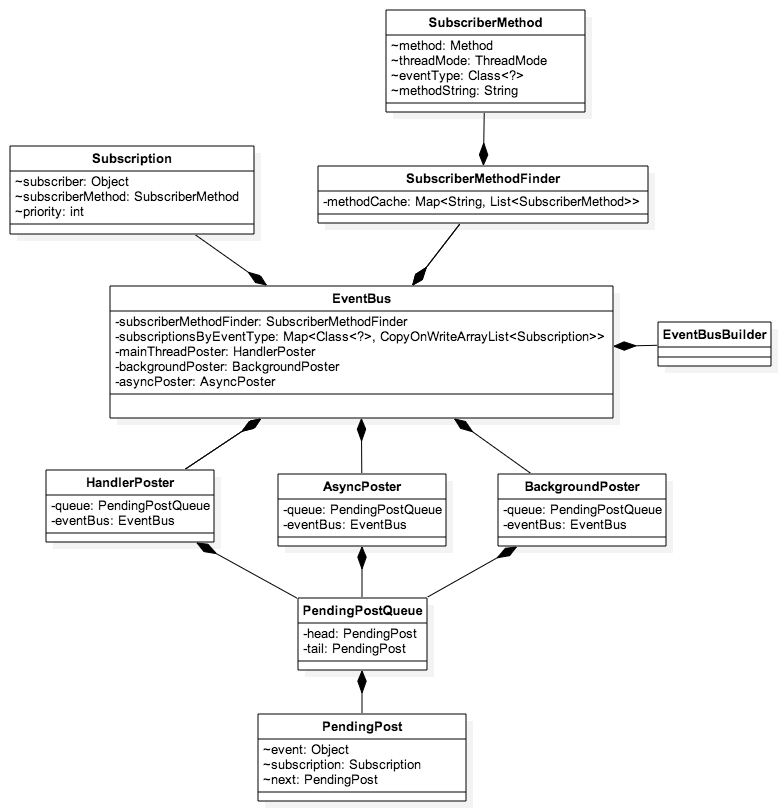
类关系图如下:
register
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public void register(Object subscriber) {
Class<?> subscriberClass = subscriber.getClass();
List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = subscriberMethodFinder.findSubscriberMethods(subscriberClass);
synchronized (this) {
for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : subscriberMethods) {
subscribe(subscriber, subscriberMethod);
}
}
}
该函数会根据订阅者的类名去subscriberMethodFinder查找当前订阅者的所有响应方法。具体是获取有注解@Subscribe的方法,同时方法必须是public不能为static、abstract。接着循环每个响应方法,依次执行subscribe。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
private void subscribe(Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) {
Class<?> eventType = subscriberMethod.eventType;
Subscription newSubscription = new Subscription(subscriber, subscriberMethod);
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);
if (subscriptions == null) {
subscriptions = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
subscriptionsByEventType.put(eventType, subscriptions);
} else {
if (subscriptions.contains(newSubscription)) {
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriber.getClass() + " already registered to event "
+ eventType);
}
}
int size = subscriptions.size();
for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
if (i == size || subscriberMethod.priority > subscriptions.get(i).subscriberMethod.priority) {
subscriptions.add(i, newSubscription);
break;
}
}
List<Class<?>> subscribedEvents = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);
if (subscribedEvents == null) {
subscribedEvents = new ArrayList<>();
typesBySubscriber.put(subscriber, subscribedEvents);
}
//暂存
subscribedEvents.add(eventType);
//处理sticky事件,如果之前有发布对应的sticky事件则在当前subscriber注册之后去触发对应的方法。
if (subscriberMethod.sticky) {
if (eventInheritance) {
// Existing sticky events of all subclasses of eventType have to be considered.
// Note: Iterating over all events may be inefficient with lots of sticky events,
// thus data structure should be changed to allow a more efficient lookup
// (e.g. an additional map storing sub classes of super classes: Class -> List<Class>).
Set<Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object>> entries = stickyEvents.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> entry : entries) {
Class<?> candidateEventType = entry.getKey();
if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(candidateEventType)) {
Object stickyEvent = entry.getValue();
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);
}
}
} else {
Object stickyEvent = stickyEvents.get(eventType);
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);
}
}
}
subscribe通过subscriptionsByEventType得到该事件类型所有订阅者信息队列,根据优先级将当前订阅者信息插入到订阅者队列subscriptionsByEventType中。
在typesBySubscriber中得到当前订阅者订阅的所有事件队列,将此事件保存到队列typesBySubscriber中,用于后续取消订阅;
检查这个事件是否是 Sticky 事件,如果是则从stickyEvents事件保存队列中取出该事件类型最后一个事件发送给当前订阅者。
post
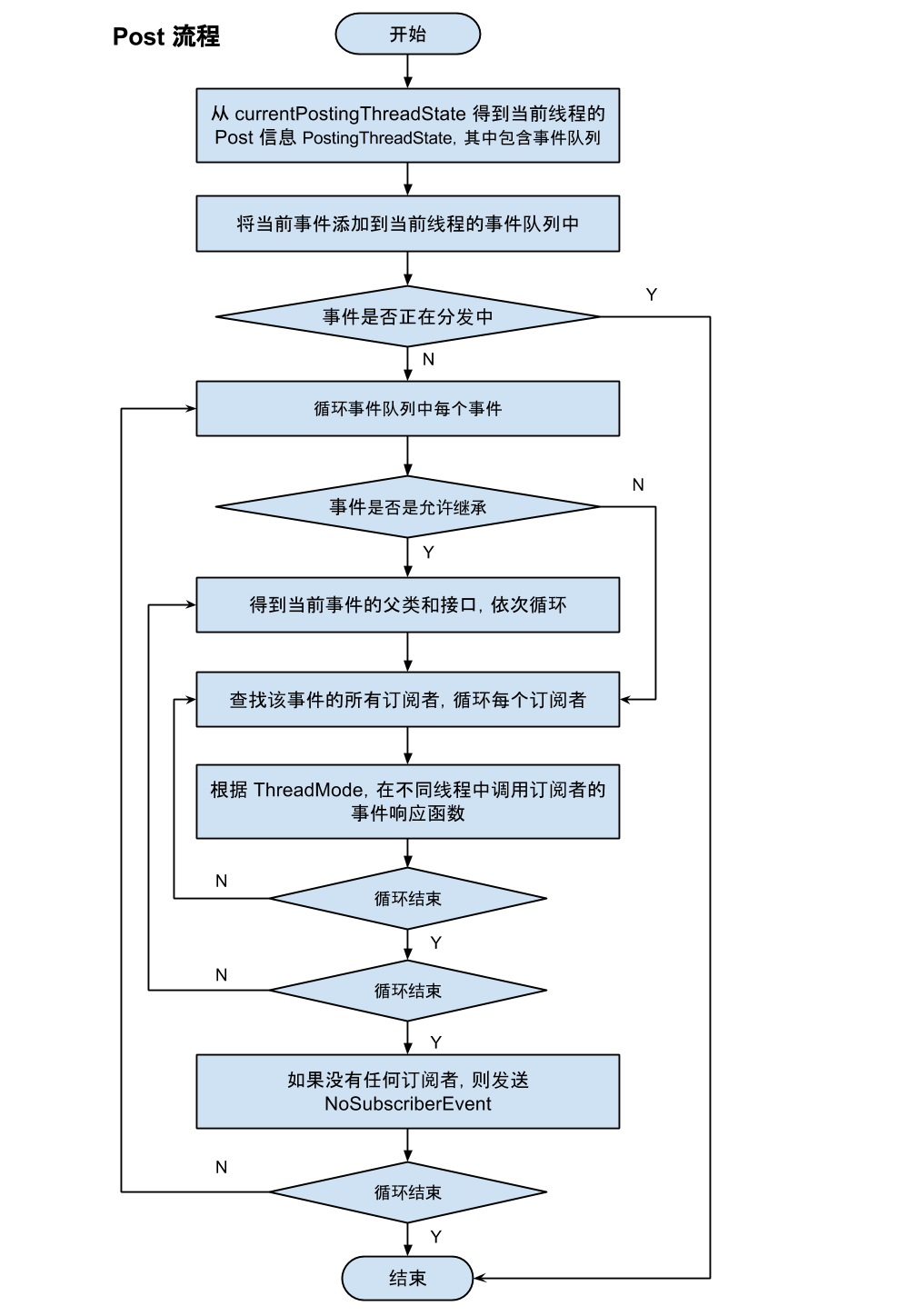
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
public void post(Object event) {
//从ThreadLocal中取出当前的PostingThreadState
PostingThreadState postingState = currentPostingThreadState.get();
//获取事件队列
List<Object> eventQueue = postingState.eventQueue;
//添加事件到事件队列中
eventQueue.add(event);
if (!postingState.isPosting) {
//判断当前是否是主线程
postingState.isMainThread = isMainThread();
postingState.isPosting = true;
if (postingState.canceled) {
throw new EventBusException("Internal error. Abort state was not reset");
}
try {
while (!eventQueue.isEmpty()) {
//具体调用方法
postSingleEvent(eventQueue.remove(0), postingState);
}
} finally {
postingState.isPosting = false;
postingState.isMainThread = false;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
private void postSingleEvent(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState) throws Error {
Class<?> eventClass = event.getClass();
boolean subscriptionFound = false;
//EventBus提供的DEFAULT_BUILDER中,这个参数为true,是否从父类查找对应的@subscribe方法。
if (eventInheritance) {
List<Class<?>> eventTypes = lookupAllEventTypes(eventClass);
int countTypes = eventTypes.size();
for (int h = 0; h < countTypes; h++) {
Class<?> clazz = eventTypes.get(h);
//继续调用
subscriptionFound |= postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, clazz);
}
} else {
subscriptionFound = postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, eventClass);
}
//如果没有@subscribe方法
if (!subscriptionFound) {
if (logNoSubscriberMessages) {
logger.log(Level.FINE, "No subscribers registered for event " + eventClass);
}
//sendNoSubscriberEvent表示是否继续发送没有接收者的Event,默认为true。
if (sendNoSubscriberEvent && eventClass != NoSubscriberEvent.class &&
eventClass != SubscriberExceptionEvent.class) {
post(new NoSubscriberEvent(this, event));
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
private boolean postSingleEventForEventType(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState, Class<?> eventClass) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions;
synchronized (this) {
//这个在调用register会先put对应的eventClass。
subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventClass);
}
if (subscriptions != null && !subscriptions.isEmpty()) {
for (Subscription subscription : subscriptions) {
postingState.event = event;
postingState.subscription = subscription;
boolean aborted = false;
try {
//这里继续调用
postToSubscription(subscription, event, postingState.isMainThread);
aborted = postingState.canceled;
} finally {
postingState.event = null;
postingState.subscription = null;
postingState.canceled = false;
}
if (aborted) {
break;
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
private void postToSubscription(Subscription subscription, Object event, boolean isMainThread) {
//该方法都会根据反射去调用对应的方法。
switch (subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode) {
//默认线程
case POSTING:
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
break;
//主线程
case MAIN:
if (isMainThread) {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
} else {
mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
}
break;
//主线程有序调用
case MAIN_ORDERED:
if (mainThreadPoster != null) {
mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
} else {
// temporary: technically not correct as poster not decoupled from subscriber
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
}
break;
//后台线程
case BACKGROUND:
if (isMainThread) {
backgroundPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
} else {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
}
break;
//异步
case ASYNC:
asyncPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown thread mode: " + subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode);
}
}
以上代码就是EventBus post的大致流程。
unregister
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public synchronized void unregister(Object subscriber) {
List<Class<?>> subscribedTypes = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);
if (subscribedTypes != null) {
for (Class<?> eventType : subscribedTypes) {
unsubscribeByEventType(subscriber, eventType);
}
typesBySubscriber.remove(subscriber);
} else {
logger.log(Level.WARNING, "Subscriber to unregister was not registered before: " + subscriber.getClass());
}
}
private void unsubscribeByEventType(Object subscriber, Class<?> eventType) {
List<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);
if (subscriptions != null) {
int size = subscriptions.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Subscription subscription = subscriptions.get(i);
if (subscription.subscriber == subscriber) {
subscription.active = false;
subscriptions.remove(i);
i--;
size--;
}
}
}
}
该方法总结一下就是清除之前register的遗留信息。
Sticky事件
一般的事件post之后,在post之后注册的接收者无法接收到该事件,鉴于这种情况,有了Sticky事件,Sticky事件post之后,在之后注册的接收者依然能够接收到该事件。
在源码中的实现如下:
EventBus#postSticky(object)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public void postSticky(Object event) {
synchronized (stickyEvents) {
//这里会暂存sticky事件
stickyEvents.put(event.getClass(), event);
}
//调用正常的post流程
post(event);
}
再回到EventBus#register()方法中调用的subscribe()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
private void subscribe(Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) {
xxx
//处理sticky事件,如果之前有发布对应的sticky事件则在当前subscriber注册之后去触发对应的方法。
if (subscriberMethod.sticky) {
if (eventInheritance) {
//获取暂存的对应sticky事件
Set<Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object>> entries = stickyEvents.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> entry : entries) {
Class<?> candidateEventType = entry.getKey();
if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(candidateEventType)) {
Object stickyEvent = entry.getValue();
//触发对应的接收者方法
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);
}
}
} else {
Object stickyEvent = stickyEvents.get(eventType);
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);
}
}
}
如果想移除sticky事件的话,只需要调用
1
EventBus.getDefault().removeStickyEvent(stickyEvent)
对应EventBus中的源码:
1
2
3
4
5
public <T> T removeStickyEvent(Class<T> eventType) {
synchronized (stickyEvents) {
return eventType.cast(stickyEvents.remove(eventType));
}
}